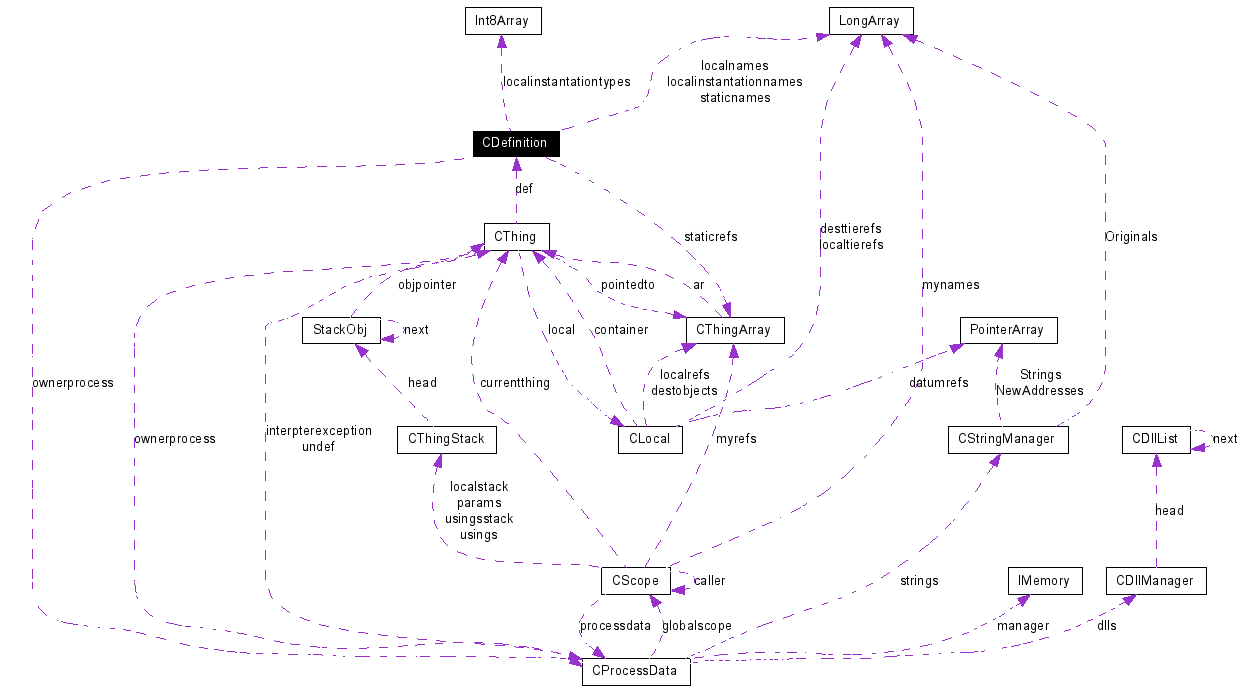
Collaboration diagram for CDefinition:

Public Member Functions | |
| void | Construct (CProcessData *owner) |
| The Construct function sets up the internal structure of the CDefinition object. | |
| void | Destruct () |
| The Destruct function properly de-allocates and cleans up the internal structure of a CDefinition. | |
Public Attributes | |
| long | refcount |
| the number of references to this definition, a defintion is released when there are no references | |
| LongArray | staticnames |
| the names of the statics as indexes in a sting table | |
| CThingArray | staticrefs |
| pointers to CThings that are the static references | |
| LongArray | localnames |
| the names of the local members as indices into a string table | |
| LongArray | localinstantationnames |
| The name, if any that a given local need to instantiate or reference upon being created. | |
| Int8Array | localinstantationtypes |
| The way that each local should be created, for example as a reference, instance, ect. | |
| unsigned long | codelegth |
| the length of the byte code data | |
| __int8 * | code |
| pointer to byte code data) | |
| CProcessData * | ownerprocess |
| the process this CDefintion belongs to, is always valid and non-null | |
| HANDLE | mutex |
| the unique mutex for this CDefinition | |
All CThings are associated with a CDefinition, but a CDefinition may be pointed to by more than one CThing. CDefinitions have their own internal refernce counting mechanism. CDefinitions each have an internal mutex that should be acquired before using their member variables.
|
|
The Construct function sets up the internal structure of the CDefinition object. If you create a CDefinition though a call to malloc or new you must call its construct function after creating it. The Construct function is properly used by any functions in this API that returns a new CDefintion.
|
|
|
The Destruct function properly de-allocates and cleans up the internal structure of a CDefinition. If you are manually destroying a CDefinition by any method you must call Destruct on it before doing so. Failure to call Destruct will cause memory leaks.
|
 1.4.2
1.4.2